During the COVID-19 outbreak, the temporary closure of offline stores resulted in a boost to e-commerce in China as people shifting toward more online shopping. The increase in attention on the online landscape among consumers has created opportunities in China’s e-commerce sector following COVID-19.
Foreign brands looking to enter the Chinese market or establish new online sales channels are encouraged to take notice of the new trends emerging in China following COVID-19.
Growth in e-commerce in China by platform
The three largest e-commerce platforms in China, Pinduoduo, Tmall, and JD, have all seen enormous growth in sales over the past year. Tmall sales of physical goods had a year-on-year growth rate of 10% in Q1 2020. Excluding unpaid orders, the growth rate was 23% year-on-year. JingDong grew by 24% in terms of the total value of all orders, totaling 2.08 trillion RMB at the end of 2019, and Pinduoduo saw an increase in sales of 108% from 557 billion RMB in Q1 2019 to 1.15 trillion RMB in Q1 of 2020.
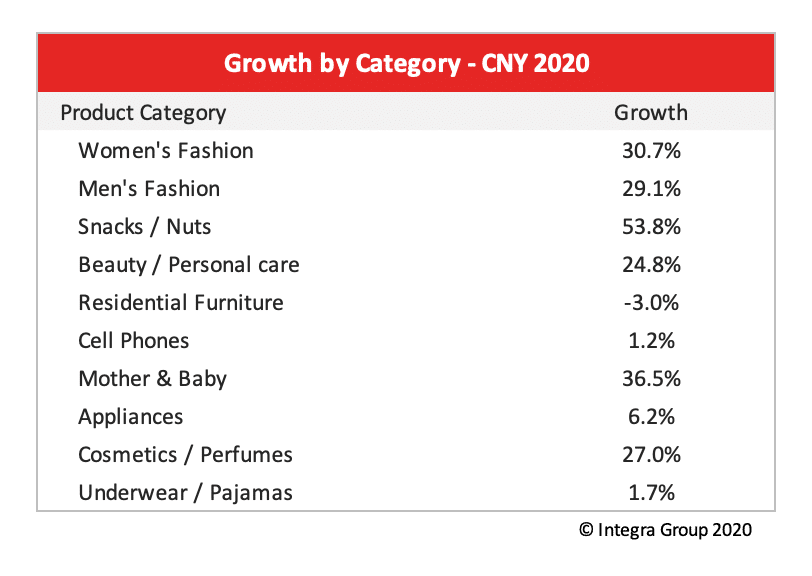
Consumer purchase through Taobao and Tmall across categories also grew at considerable rates during Chinese New Year, a trend that brands should take note of for their future success.
Social e-commerce in China
Social e-commerce refers to the uses of social elements to drive online sales and has rapidly been gaining popularity in China. The two main platforms that are known for their use of social e-commerce include Xiaohongshu (LRB) and Pinduoduo.
According to a report released by China Internet Watch (CIW) in August 2019, the total volume of sales from social e-commerce reached 626 billion RMB in 2018 and is predicted to increase to 2.06 trillion RMB by the end of 2020. From 2015 to 2018, social e-commerce increased its share of the online e-commerce market from just 0.1% to 7.8%. These figures demonstrate the explosive growth of this new form of entertainment shopping and provide an opportunity for brands to encourage purchase among customers through social interaction.
How to get started on major e-commerce platforms in China
Setting up a store on one of the major e-commerce platforms generally consists of the following four steps.
1. Application Submission. (Estimated time: 1 working day)
When completing the application, brand representatives need to choose the type of store, select the category of products, and prepare all of the brand information and documents required, then submit the application online.
2. Verification (Estimated time: 7 working day)
The application verification includes a qualification of the applications by the e-commerce platform according to the documents submitted.
3. Prepare for store opening. (Estimated time: 7-14 working days)
Preparing for the store opening involves activating the account by making the appropriate payments, such as the deposits and annual service fees. Companies should prepare the product pages and ensure that the store navigation and design is intuitive and. Companies should also synchronize logistics and distribution to be consistent with the e-commerce platform and prepare the customer service staff for the official launch.
4. Official launch (Estimated time: 3 working days)
The official launch will include the launch of product sales and of any marketing plans to increase traffic to the store. The sales volume and customer comments on a store are used as indications of the store’s popularity and reputation, therefore increasing initial traffic and sales is crucial to its long-term success.

Time requirements:
If brands meet all of the platform administration requirements, setting up an e-commerce store takes between 3 to 5 weeks. However, this time frame does not take into account the time required to set up logistics and distribution.
Cross-border e-commerce
Foreign businesses that do not wish to establish a physical presence in China can also choose to supply their products through cross-border e-commerce channels.
Cross-border e-commerce enables foreign businesses to supply their product on China’s e-commerce platforms like TMall, JD, and Taobao, without any direct investment or the need to be physically present in China. To start, businesses should prepare by registering their trademark in China and begin conducting due diligence on e-commerce agents who can assist them on the ground.
The only technical qualification for a cross-border e-commerce agent in China is their scope of business allows them to engage in such services. Foreign companies can verify this by inspecting the agent business scope on a Chinese company registry, or by confirming whether the agent engages in such services for other overseas clients.
The foreign enterprise must then prepare an agreement with the Chinese agent authorizing them to act as an agent on their behalf. The agent will then complete the registration on your behalf in a cross-border e-commerce pilot zone together with the customs, tax, and the accounting and bookkeeping registration。
Current cross-border e-commerce pilot programs and zones have been expanding in China. These pilot zones provide various benefits for foreign and local companies engaging in cross-border e-commerce including standardized procedures, VAT and consumption tax exemptions for retail exports, reduced CIT, and various other benefits provided by local governments.
How Integra can help
Integra can assist foreign companies looking to supply their products on the Chinese market from start to finish. Our clients benefit from expertise in taxation, administration, and business operations in China when deciding on the right course of action for entering the Chinese market – ensuring all needs and precautions are taken into account.







