Chinese authorities have used a system of Negative Lists and Encouraged Lists to guide foreign investments in specific industries in need of foreign investment and know-how. The 2020 Encouraged Catalogue and the 2020 Negative Lists come as good news for foreign investors in the form of greater market access and expanding the number of industries where foreign investment is eligible for preferential treatment.
The 2020 Encouraged Catalogue saw an increase of 127 items, an increase of 10% over its predecessor, bringing the total to 1235 items. Meanwhile, the number of items on the Negative List has been reduced from 33 to 30.
The increased number of items on the Encouraged Catalogue and simultaneous reduction of the Negative list is a move by authorities to stabilize foreign investment and deliver on promises made during the most recent “Two Sessions” held by the National Committee of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC) to further open up the Chinese economy to foreign investors.
Below is a summary of the lists maintained by Chinese authorities that foreign investors should pay attention to prior to investing in China.
Catalogue of Industries Encouraged for Foreign Investment (“Encouraged Catalogue”) – a list of industries and business activities where foreign investment is encouraged and eligible for preferential treatment (available here). The Encourage list consists of two sections:
- National List – outlines industries and business activities where foreign investment is encouraged and eligible for preferential treatment nationwide.
- Central, Western, and Northeastern Regional List (“Regional List”) – outlines industries and business activities where foreign investment is encouraged and eligible for preferential treatment by region. Regions include Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning, Jilin, Heilongjiang, Anhui, Jiangxi, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Guangxi, Hainan, Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Tibet, Jiangxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang.
Special Administrative Measures for Foreign Investment Access (“Negative List”) – Prohibits or restricts (by means of equity investment or other forms) foreign investment by industry nationwide – outside of Pilot Free Trade Zones (available here).
Special Administrative Measures for Foreign Investment Access to Pilot Free Trade Zones (“FTZ Negative List”) – Prohibits or restricts (by means of equity investment or other forms) foreign investment by industry within Pilot Free Trade Zones (available here) .
The Negative List of Market Access (“MA Negative List”) – Market regulations restricting industry access for all enterprises in China (foreign and domestic) including state-owned enterprises, private enterprises, join-ventures, and non-resident enterprises (available here).
- Prohibited – prohibits market access to certain industries and prevents enterprises from engaging in specific activities which violate laws, regulations, and State Council Decisions.
- Restricted – restricts market access through licensing, obtaining special permits, and attaining other legal qualifications prior to market entry.
Notable Changes to the 2020 Encouraged Catalogue
Compared to the 2019 Encouraged Catalogue, the 2020 edition adds a total of 127 items, 65 items to the National List and 62 items to the Regional List, bringing the total number of items to 1235. In addition, 88 existing items were modified.
The changes to the 2020 Encouraged Catalogue take manufacturing as the key sector to encourage foreign investment including advanced manufacturing and supply chains, production-oriented services, and a focus on China’s central, western, and northeastern regions.
Advanced manufacturing and supply chains – additions in areas of raw material such hydrofluoric acid, hydrogen fluoride, special glass fibers, etc.; additions and modifications in areas of components such as high-pressure vacuum components, valves, wheel speed sensors, etc.; and additions or modifications in the area of end products such as integrated circuit test equipment, laser projection equipment, Ultra HD televisions, ventilators, AI-assisted medical equipment, etc.
Production-oriented services – additions and modifications in areas of R&D such as high-technology equipment, 5G telecommunications, design of sewage treatment facilities, blockchain technology, etc.; additions and modifications to business services such as high-end equipment maintenance, transformation and integration of digital production lines, industrial service network platform, etc.; and additions and modifications to logistics services such as commodity import and export distribution centers, last-mile delivery services, etc.
Central, Western, and Northeastern Regions – individual regions added and modified specific items on the Regional List in areas such as agriculture, tourism, medical equipment, active pharmaceutical ingredient production, semiconductors, vocational education, etc.
According to officials at the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), foreign-invested enterprises have created about 1/4 of China’s industrial output value, 1/5 of tax revenue, 1/15 of employment, and contribute about 40% of China’s total import and export volume. The expansion of the Encouraged Catalogue is an important policy measure by Chinese authorities to guide foreign investment in areas in need of foreign capital and know-how.
In the past, the Encouraged Catalogue has been updated once every 3 to 5 years. However, the 2020 edition comes just one year after its predecessor, the fastest ever update to the Encourage List since its inception. According to a spokesperson at the NDRC, the timely update is an effort to stabilize foreign trade and investment in response to the global decline in FDI, which saw a decrease of 40% YoY in 2020.
Additionally, the focus on manufacturing and production sectors has led many to expect advanced manufacturing to be a key focus of China’s 14th 5-year plan which is to be released later this year.
Preferential Policies for Foreign Investment in Encouraged Industries
Investment in industries and business activities outlined in the 2020 Encouraged Catalogue are eligible for preferential treatment including;
- Customs duty exemptions – equipment imported for self-use for encouraged foreign-investment projects may be exempt from customs duty upon import within the total investment.
- Land-use priority and preferential pricing – Land-intensive foreign investment projects within the scope of the Encouraged Catalogue may be granted priority land-use allocation. Additionally, the land-use price may be fixed at 70% of the national minimum price for the transfer of industrial land at the same level or higher.
- Reduced corporate income tax rate – Encouraged foreign investment projects in China’s Western, Central, and Northeastern areas within the scope of the Regional List can enjoy a reduced CIT rate of 15%, down from 25%.
In order for encouraged foreign-investment projects to qualify for the benefits provided above, at least 60% of the new enterprise’s revenue must fall within the scope of business activity provided under the Encouraged Catalogue.
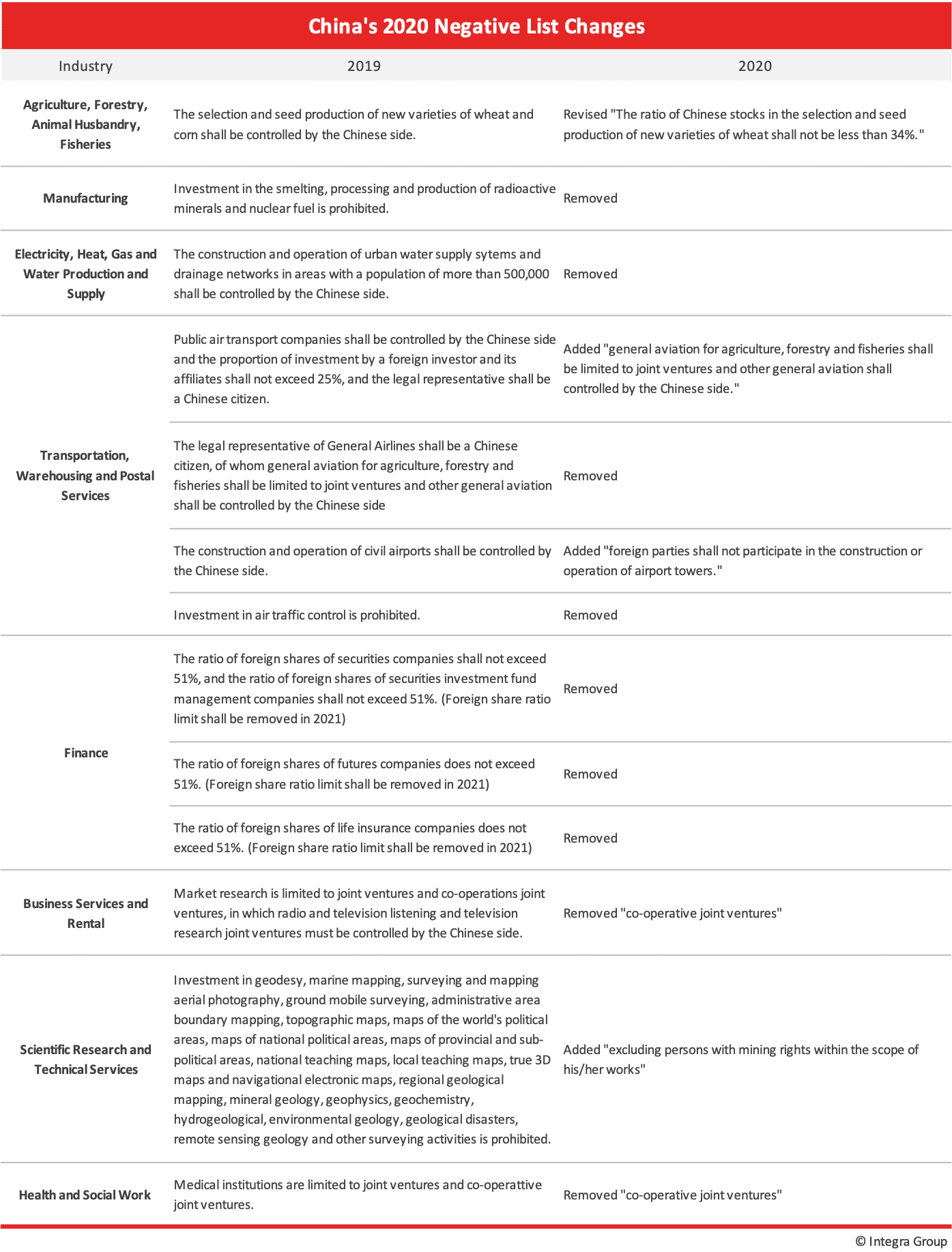
Notable Changes to the 2020 Negative Lists
The two negative lists refer to the Negative List for Foreign Investment (“Negative List”), applicable nationwide, and the Free Trade Zone Negative List for Foreign Investment (“FTZ Negative List”), applicable to Free Trade Zones across China.
The 2020 Negative list for foreign investment and the 2020 FTZ Negative List were shortened, delivering on a promise made during the 2020 Two Sessions held in Beijing last year. Notably, restrictions on foreign investment in the finance sector have been removed entirely – providing foreign-invested enterprises equal market access.
A detailed list of the changes made to the 2020 Negative list can be found below.
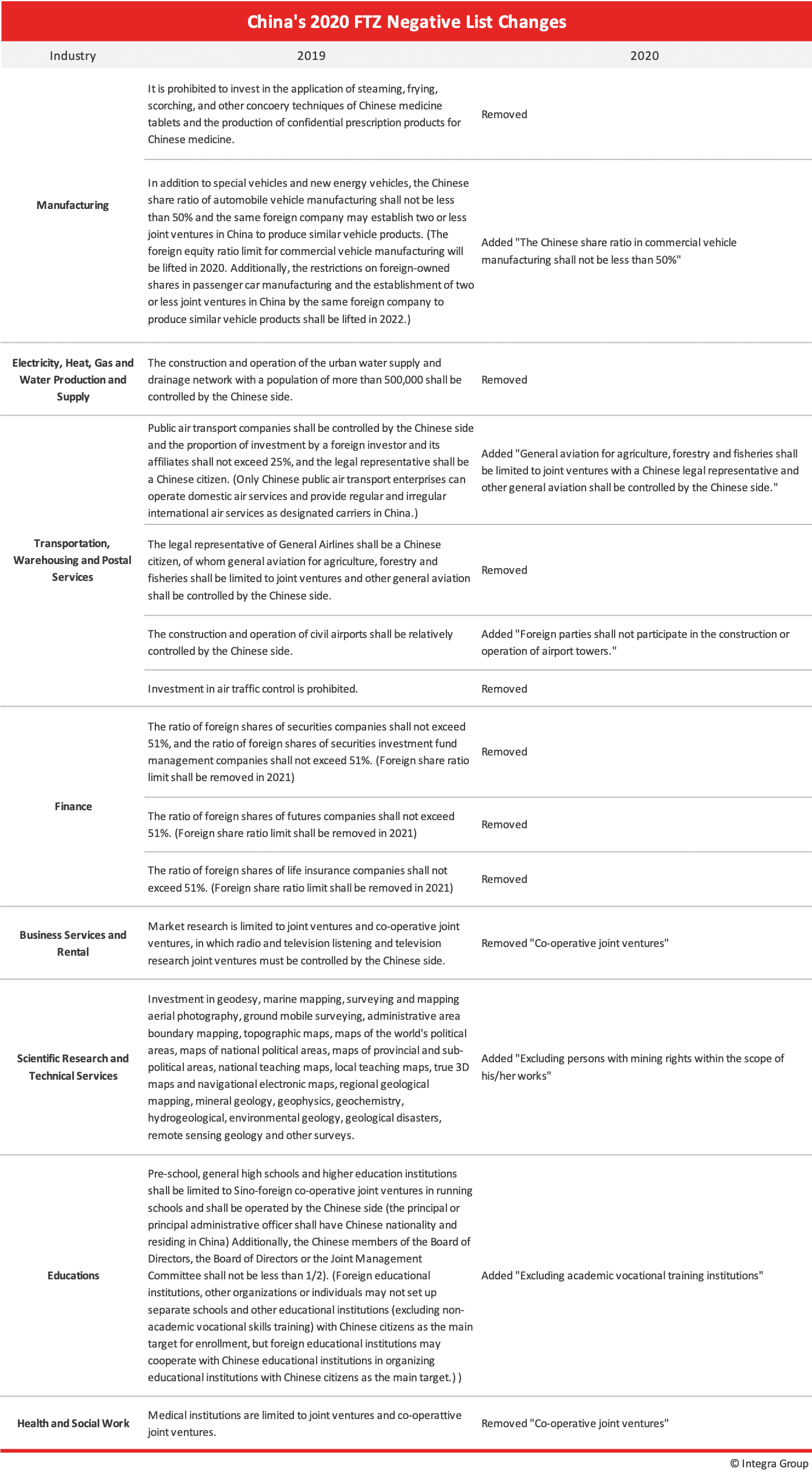
A detailed list of the changes made to the 2020 FTZ Negative list can be found below.
Notable Changes to the 2020 MA Negative List
The Negative List for Market Access (“MA Negative List”) outlines industries that are either prohibited or restricted for all enterprises in China (foreign and domestic) including state-owned enterprises, private enterprises, joint-ventures, and non-resident enterprises. The 2020 MA Negative list includes 123 items, consisting of 118 restricted items and 5 prohibited items.
Industries and business activities outlined as prohibited prevent enterprises from engaging in said industries or activities in any form. The 2020 MA Negative List provides 5 industries and business activities which are outlined as prohibited, as follows:
- Industries and business activities clearly prohibited by laws, regulations, or decisions by the State Council;
- Products, technologies, processes, equipment, and behaviors that are expressly prohibited and restricted by state industrial policies;
- All development activities that do not meet the requirements of their main functional area outlined by the state;
- Financial-related business activities in violation of the law; and,
- Internet-related business activities in violation of the law.
Additionally, industries and business activities outlined as restricted require enterprises to seek special government approvals or licensing prior to investment.
Changes made to the 2020 MA Negative list include 21 revisions, 1 addition, 3 removed, and 6 items merged concerning restricted industries and business activities.
Notably, the large-scale transfer of land management rights has been added to the list of restricted business activities – and enterprises must seek government approval before engaging in the sale or transfer of large-scale land management rights.
Revisions to the 2020 MA Negative List were largely in the area of Manufacturing and Agriculture with both liberalization and tightening of regulations on enterprises engaged in specific activities. For example, in the area of manufacturing, the productions and security evaluation of commercial encryption applications has been removed while restrictions on forest and marine resources have been tightened.
Foreign Investment in 2021
The expansion of items on the Encouraged Catalogue and simultaneous reduction of items on the Negative List provide foreign investors greater market access going forward. The updated lists come just before the highly anticipated 14th 5-year plan which is to be released in March of this year. Foreign investors planning a China market entry should take notice of the changes to advanced manufacturing and the high-quality development goals of China moving forward and carefully review the lists mentioned.
Foreign investors are encouraged to seek the guidance of a market entry professional when planning their market entry strategy and fully consider their compliance requirements prior to carrying out their investment.







